Florida's Frogs
Treefrogs (Family Hylidae)
_________________________________________________________
Barking Treefrog
(Hyla gratiosa)
Barking Treefrog (click on small images to view larger)
Photos by (clockwise from top) Dr. Michael Andreu (UF), Patrick Ruegger, Dr. Steve A. Johnson (UF), and Elizabeth A. Casey Hagood. Photos may not be used without the express written permission of the photographer. To obtain permission to use photos by Dr. Johnson for educational purposes, email tadpole@ufl.edu.
Size:
Usually 2 to 2.5 in. (max 2.75 in.)
Identification:
Plump body is green, gray, or brown; skin is uniformly bumpy (like goose bumps, granular). Back is marked with dark, round spots that may fade when the frog changes color, and sometimes with small, yellow flecks. Sides may be marked with light stripes with irregular borders, as shown in the photo above. Like all treefrogs, this species has enlarged, sticky toepads.
Breeding:
March to August; lays eggs singly on the bottom of the pond. Breeding call is a hollow tonk, tonk; a chorus of frogs sounds like distant barking dogs. To hear frog calls, visit the USGS Frog Call Lookup and select the species you want to hear from the common name drop-down list.
Diet:
Beetles and other small invertebrates
Habitats:
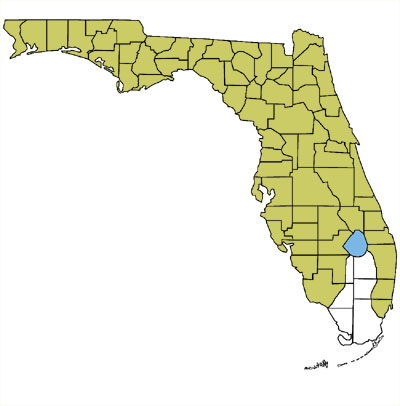
Found throughout most of Florida (except the Everglades and Keys), usually high in treetops. Has also been found burrowed in sand under logs or grass near breeding sites. Breeds in a variety of shallow wetland habitats (fish-free), including cypress domes, bogs, wet hammocks, and flooded ditches.
Map by Monica E. McGarrity - may be used freely for education.
Go Back to Florida's Frogs - All Regions