Florida's Frogs & Toads
Treefrogs (Family Hylidae)
_________________________________________________________
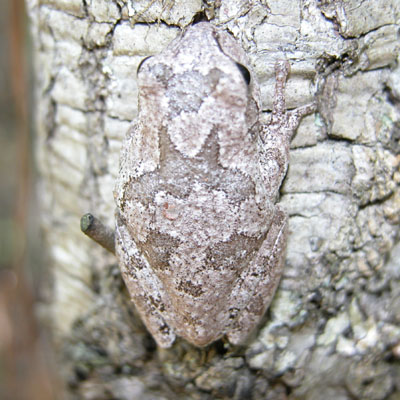
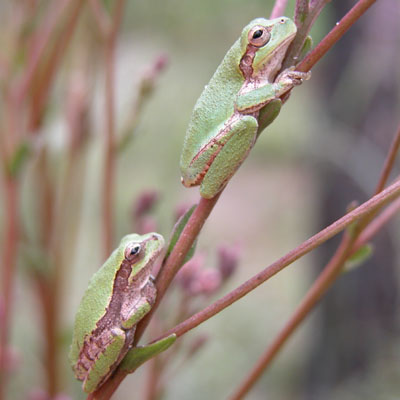
Pinewoods Treefrog
(Hyla femoralis)
Pinewoods Treefrog (click on small images to view larger)
Photos by Dr. Steve A. Johnson (UF). To obtain permission to use these photos for educational purposes, email tadpole@ufl.edu.
Size:
Usually 1 to 1.5 in.
Identification:
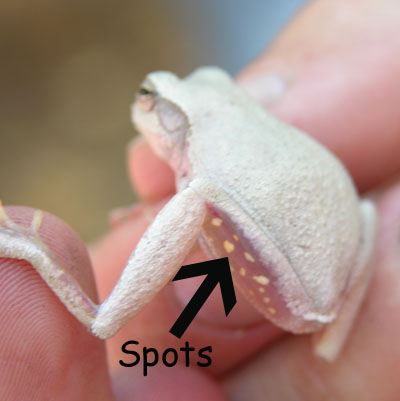
Body is tan, gray, green, or brown, and may be marked with darker blotches or irregular bands. Face is usually marked with a "bandit mask." Hidden surfaces of the thighs are marked with distinctive orange (or whitish yellow) spots (as shown in the bottom inset photo above). Like other treefrogs, this species has enlarged, sticky toepads.
Breeding:
April to October; eggs are laid in loose clusters (100-250 eggs) attached to vegetation just below the surface of the water. Call is a rapid tapping sound, like Morse code. To hear frog calls, visit the USGS Frog Call Lookup and select the species you want to hear from the common name drop-down list.
Diet:
Ants, beetles, crickets, flies, moths, spiders, wasps, and other small invertebrates.
Habitats:
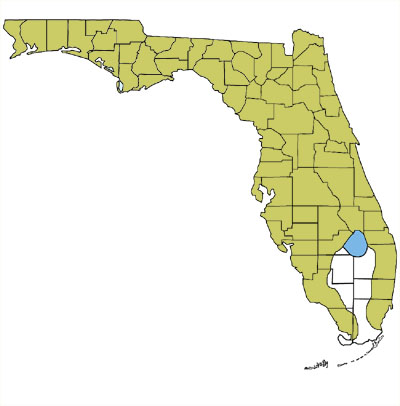
Found throughout most of Florida, with the exception of the south-central peninsula and the Keys, usually high in trees in sandhill, pine flatwoods, pine-oak forest, and cypress swamps near breeding sites. Overwinters in decaying logs or under loose bark. Breeds in shallow, fish-free wetlands, including marshes, bayheads, cypress swamps, and ditches.
Map by Monica E. McGarrity - may be used freely for education.
Go Back to Florida's Frogs - All Regions